In an era of rapid technological advancement, hospitals are evolving to become more efficient, patient-centric, and technologically integrated.

The Smart Hospital Maturity Model (SHMM), funded through the sponsorship of care.ai, now part of Stryker and with survey design and support from CHIME, provides a framework for healthcare institutions to assess their current state of digital transformation and chart a course toward becoming fully “smart” hospitals.
Over 560 data points from the 89-question survey drive the scoring of the SHMM. Any healthcare delivery provider wishing to assess their current smart care journey may complete the survey. From the completed survey, participants receive not only their scores and insights into their smart care gaps and opportunities.
A significant value of this model is providing strategic insights into a facility’s position and progress on leveraging smart care technologies. By equipping health care organization leaders with these insights, future decisions can be guided by the knowledge needed to make sound business and clinical decisions.
As facilities move further into the adoption and use of smart care technology and processes, they should begin to realize significant benefits:
Improved patient outcomes through more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatments
Enhanced operational efficiency, reducing costs and wait times
Better patient experiences, with more convenient and accessible care
Increased staff satisfaction by automating routine tasks and providing better decision support tools
Improved population health management through better data analysis and predictive capabilities
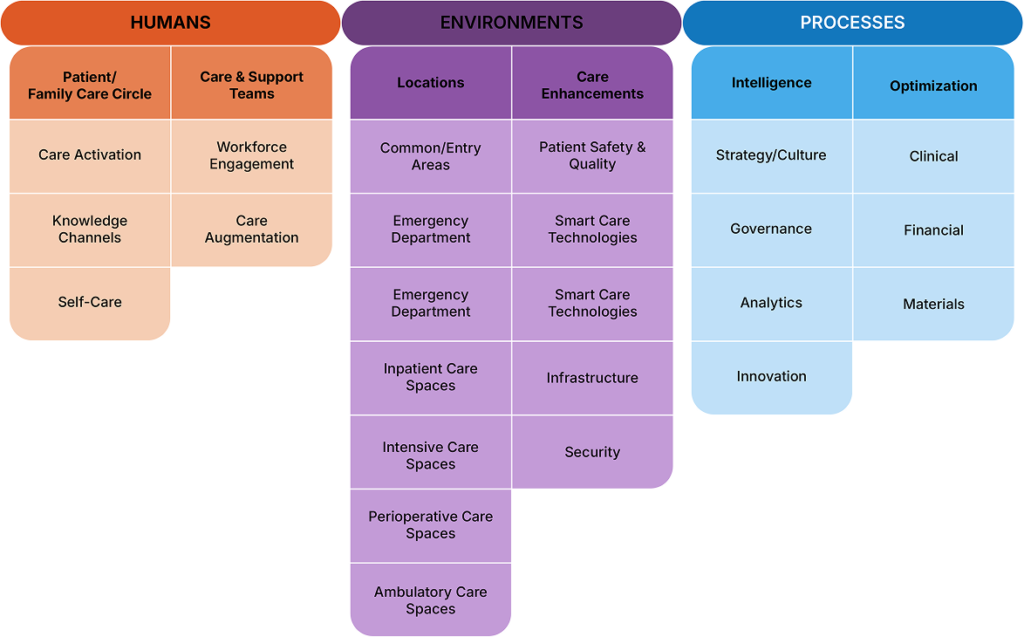
The model is designed around the three primary components of healthcare: people, places and processes.
One, the model looks at how patients and their care circles as well as clinical and support teams utilize smart technology during care.
The model’s second component, places, looks at how smart care technology has been adopted in the major clinical areas of emergency care, inpatient care, intensive care, perioperative care, and ambulatory care spaces.
The model’s third component, processes, assesses the use of smart technology in key clinical, financial, and materials workflows.

Overview:Sections, Domains and Subject Areas
The path for a health care delivery organization to an environment that fully embraces the tools and processes of intelligence-assisted care is not a fixed one.
Each organization has variables that influence the speed and direction of its journey—existing infrastructure, culture, budget, leadership, and many other factors.
However, there are ways in which to categorize the journey into stages or leaps. Generally, clinical care technologies and processes can be organized in a sequential way that illustrates the move from a completely human driven facility where care is initiated and managed only through human action to a technology driven facility where the human effort is augmented by machine analytics, intelligence and virtual care.

The smart hospital is not a facility where humans have been replaced by technology. The smart hospital is where technology is used to enhance the clinical experience such that patients are more connected to their families and practitioners and practitioners are working at the highest level of their licensure. In a smart hospital, interventions and treatment are guided by extensive analytics and may be triggered without human action. And in a smart hospital, business operations achieve high efficiency through real-time automation.
The SHMM leaps are designed with a look to the future. At its highest level, few if any facilities currently have achieved Leap 5. This is a supervised autonomous environment where clinicians manage care through an integrated system of technologies and processes; an environment where real-time analytics identify, recommend and at times initiate clinical actions. Virtual and machine-intelligence observations, monitoring, communications, and treatments are the rule.


At this level, hospitals have basic IT infrastructure in place. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are implemented, but their use may not be fully optimized. Some departments may have standalone digital solutions, but there’s limited integration across the organization. The environment consists largely of manual workflows, siloed data, and human initiation is required for all processes.
Hospitals at this stage have moved beyond basic digitization largely through disjointed technologies that provide limited assistance with specific tasks. Unintegrated point solutions and limited data sharing predominate. There is little enterprise strategy or vision regarding smart care.

Integrated and interoperable networks with data sharing support care in many care settings. Internet of Things (IoT) devices start to appear, such as smart beds and connected medical devices. Real-time location systems might be implemented for asset tracking.
Cross-functional integration create unified systems. Detailed smart care strategies and roadmaps exist. Adoption of smart care technologies are scaled across the enterprise. At this level, AI and machine learning are introduced into clinical and operational processes. Predictive and reactive analytics are used for patient risk assessment and resource allocation.

Contextualised and customized business and clinical activities actively adapt to evolving situations and individual needs. AI assists complex clinical and operational decisions. Some autonomous technology pilots emerge.
This stage represents a fully realized smart hospital. Here, all systems are interconnected, creating a seamless flow of data and insights. AI at the adaptive level is embedded throughout the organization, from clinical decision support to building management. Personalized medicine is the norm, with treatment plans tailored using genetic data and AI analysis. The patient’s experience is fully digitized, from admission to post-discharge care.
